正文
现在我们来编码。
class BinarySearchTree:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left_child = None
self.right_child = None
def insert_node(self, value):
if value <= self.value and self.left_child:
self.left_child.insert_node(value)
elif value <= self.value:
self.left_child = BinarySearchTree(value)
elif value > self.value and self.right_child:
self.right_child.insert_node(value)
else:
self.right_child = BinarySearchTree(value)
看起来很简单。
该算法的强大之处是其递归部分,即第9行和第13行。这两行代码均调用 insert_node 方法,并分别为其左孩子和右孩子使用它。第11行和第15行则在子节点处插入新节点。
我们来搜索节点值
我们现在要构建的算法是关于搜索的。对于给定的值(整数),我们会搜索出我们的二叉查找树有或者没有这个值。
需要注意的一个重要事项是我们如何定义树的插入算法。 首先我们有根节点。所有左子树的节点值都比根节点小。所有右子树的节点值都比根节点大。
让我们看一个例子。
假设我们有这棵树。
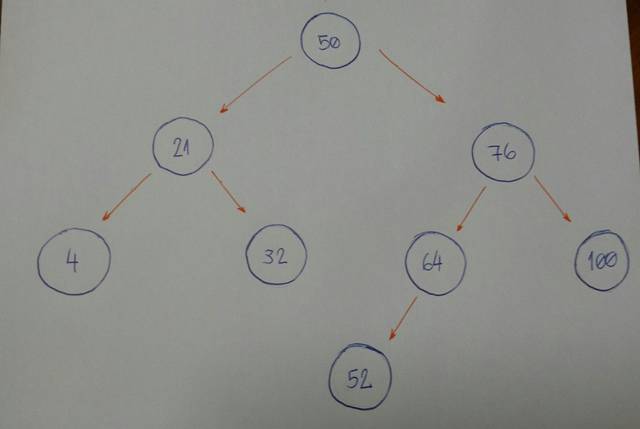
现在我们想知道是否有一个节点的值为52。
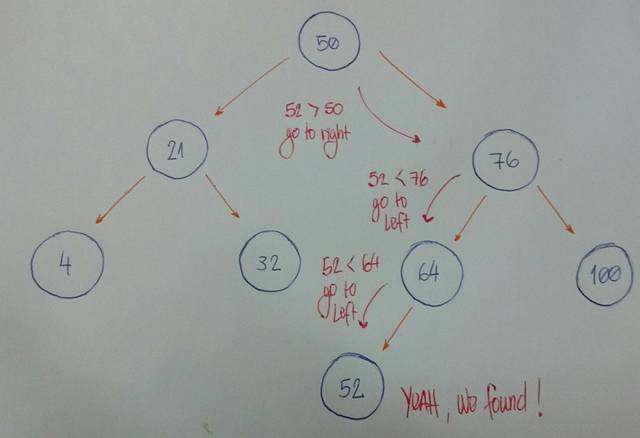
让我们把它分解。
-
我们以根节点作为当前节点开始。给定值小于当前节点值吗?如果是,那么我将在左子树上查找它。
-
给定值大于当前节点值吗?如果是,那么我们将在右子树上查找它。
-
如果规则 #1 和 #2 均为假,我们可以比较当前节点值和给定值是否相等。如果返回真,那么我们可以说:“是的,我们的树拥有给定的值。” 否则,我们说: “不,我们的树没有给定的值。”
代码如下:
class BinarySearchTree:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.left_child = None
self.right_child = None
def find_node(self, value):
if value self.value and self.right_child:
return self.right_child.find_node(value)
return value == self.value
代码分析:
-
第8行和第9行归于规则#1。
-
第10行和第11行归于规则#2。
-
第13行归于规则#3。
我们如何测试它?
让我们通过初始化值为15的根节点创建二叉查找树。
bst = BinarySearchTree(15)
现在我们将插入许多新节点。
bst.insert_node(10)
bst.insert_node(8)
bst.insert_node(12)
bst.insert_node(20)
bst.insert_node(17)
bst.insert_node(25)
bst.insert_node(19)
对于每个插入的节点,我们测试是否 find_node 方法真地管用。
print(bst.find_node(15)) # True
print(bst.find_node(10)) # True
print(bst.find_node(8)) # True
print(bst.find_node(12)) # True
print(bst.find_node(20)) # True
print(bst.find_node(17)) # True
print(bst.find_node(25)) # True
print(bst.find_node(19)) # True
是的,它对这些给定值管用!让我们测试一个二叉查找树中不存在的值。
print(bst.find_node(0)) # False
查找完毕
删除:移除和组织
删除是一个更复杂的算法,因为我们需要处理不同的情况。对于给定值,我们需要删除具有此值的节点。想象一下这个节点的以下场景:它没有孩子,有一个孩子,或者有两个孩子。
# |50| |50|
# / \ / \
# |30| |70| (DELETE 20) ---> |30| |70|
# / \ \
# |20| |40| |40|
如果要删除的节点没有子节点,我们简单地删除它。该算法不需要重组树。
# |50| |50|
# / \ / \
# |30| |70| (DELETE 30) ---> |20| |70|
# /
# |20|
在这种情况下,我们的算法需要使节点的父节点指向子节点。如果节点是左孩子,则使其父节点指向其子节点。如果节点是右孩子,则使其父节点指向其子节点。
# |50| |50|
# / \ / \
# |30| |70| (DELETE 30) ---> |40| |70|
# / \ /
# |20| |40| |20|
当节点有两个孩子,则需要从该节点的右孩子开始,找到具有最小值的节点。我们将把具有最小值的这个节点置于被删除的节点的位置。
是时候编码了。
def remove_node(self, value, parent):
if value self.value and self.right_child:
return self.right_child.remove_node(value, self)
elif value > self.value:
return False
else:
if self.left_child is None and self.right_child is None and self == parent.left_child:
parent.left_child = None
self.clear_node()
elif self.left_child is None and self.right_child is None and self == parent.right_child:
parent.right_child = None
self.clear_node()
elif self.left_child and self.right_child is None and self == parent.left_child:
parent.left_child = self.left_child
self.clear_node()
elif self.left_child and self.right_child is None and self == parent.right_child:
parent.right_child = self.left_child
self.clear_node()
elif self.right_child and self.left_child is None and self == parent.left_child:
parent.left_child = self.right_child
self.clear_node()
elif self.right_child and self.left_child is None and self == parent.right_child:
parent.right_child = self.right_child
self.clear_node()
else:
self.value = self.right_child.find_minimum_value()
self.right_child.remove_node(self.value, self)
return True
-
首先: 注意下参数 value 和 parent 。我们想找到值等于该 value 的 node ,并且该 node 的父节点对于删除该 node 是至关重要的。





